Introduction to Greenhouse Gardening
One of the best ways to grow plants year-round, no matter what the weather outside is like, is in a greenhouse. A greenhouse provides a controlled environment for optimal plant growth,
whether you’re growing fresh vegetables in the middle of winter or shielding delicate flowers from strong winds. By understanding the essentials of greenhouse gardening—from structure selection to climate control—you can create a thriving plant haven that maximizes yields and minimizes environmental stress.
Why Grow Your Own Food in a Greenhouse?
The numerous advantages that greenhouse gardening provides to both hobbyists and commercial growers are what make it appealing:
- Year-Round Production – Grow crops even in winter months.
2. Controlled Environment: Control light, humidity, and temperature.
3. Extended Growing Seasons – Start seedlings earlier and harvest later.
4. Reduce crop losses caused by frost, wind, or heavy rain by providing protection from pests and harsh weather.
5. Increased Variety of Plants: Grow non-native or exotic species.
Idea for an image: photo comparison of crops grown outdoors and those grown in a greenhouse side by side.
Types of Greenhouses
A crucial step in greenhouse gardening success is selecting the appropriate greenhouse.
1. Glass Greenhouses Advantages:
- Good light transmission and pleasing appearance.
- Cons: Fragile, higher initial cost.
2. Greenhouses made of polycarbonate Advantages:
- Lightweight, great insulation, and shatterproof.
- Cons: May fade over time.
3. Plastic Film Greenhouses Benefits:
- Affordable and simple to assemble.
- Cons: Needs to be replaced every few years; shorter lifespan.
4. Cold Frames Pros: Compact, portable, great for beginners. Cons: Limited control and space.
Image Suggestion: A graph or infographic outlining the advantages and disadvantages of various greenhouse types.
Planning Your Garden in a Greenhouse You need a clear plan before building or buying.
1. Choosing a Location Place in a location that gets the most sunlight (preferably south-facing). Ensure good drainage to prevent waterlogging.
2. Size and Shape For personal use, smaller sizes; for business use, larger sizes. Consider future expansion.
3. Floor and Foundation Concrete, gravel, or compacted soil are options. Good flooring improves drainage and reduces pests.
4. Ventilation Proper airflow prevents mold, mildew, and overheating.

Essential Tools for Growing in a Greenhouse
Having the right tools in your greenhouse will help you keep the environment for growing plants at its best. Heating Systems
- Electric heaters for controlling the temperature precisely. Gas heaters for larger setups.
- Cooling Techniques Fans for ventilation. Shades during the summer. Lighting
- LED grow lights for supplemental lighting during shorter days. Irrigation
- Drip irrigation systems keep the foliage dry and save water.

Soil and Growing Mediums
The growing medium you choose has a big impact on how healthy your plants are. Traditional Gardening with Soil Use soil that is good and full of nutrients. Regularly test for pH and nutrient balance.
Mediums That Taste Bad Vermiculite, perlite, or coconut coir for hydroponic systems Idea for an image: A close-up image of various containers containing labeled greenhouse growing media. Popular Crops for Greenhouse Gardening
Certain plants thrive particularly well in greenhouse environments: Tomatoes adore the constant humidity and warmth. Cucumbers: Vertical growing techniques are advantageous. Peppers thrive when temperatures remain constant. Lettuce and Leafy Greens – Quick, repeat harvests.
Herbs like cilantro, basil, and mint do well indoors. Idea for an image: Collage of different greenhouse-grown crops. Climate Control in Greenhouse Gardening
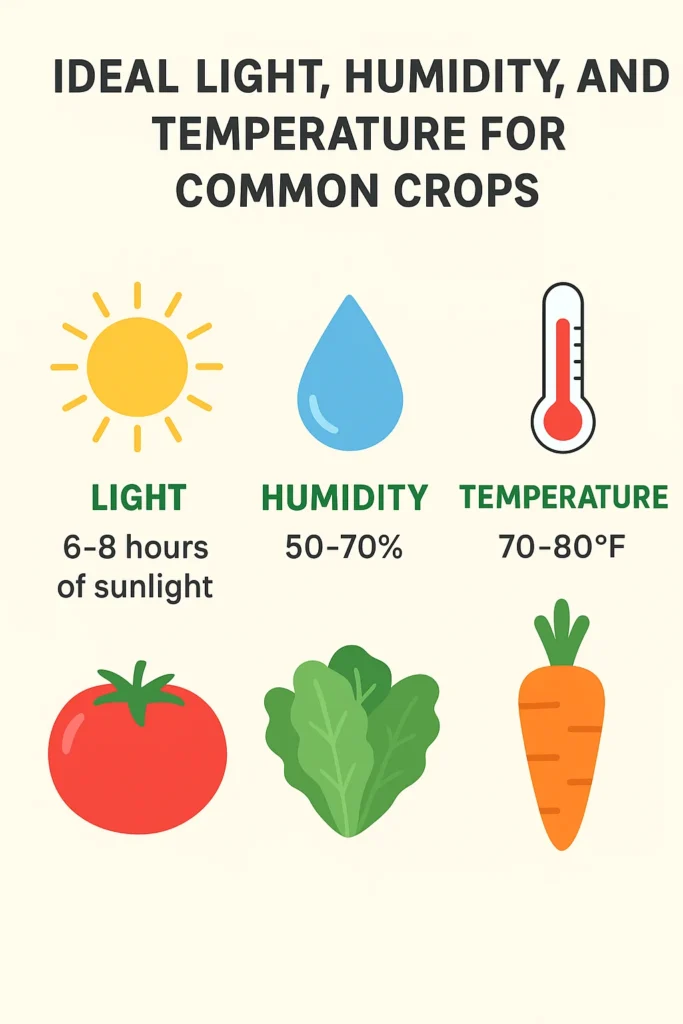
For successful greenhouse gardening, it is essential to control light, temperature, and humidity. Temperature Management For most crops, the ideal range is 65–75°F (18–24°C). Use thermostats for automatic adjustments.
Humidity Control
Keep the relative humidity at 50-70%. Avoid excess moisture to prevent fungal diseases.
Lighting Control Make use of reflective surfaces to get the most sunlight. Use grow lights in low-light months.
Common Greenhouse Pests:
Aphids
Whiteflies
Insect mites Tips for Preventing Disease: Before using tools and pots, sterilize them. Rotate your crops regularly. Plants that are ill should be removed right away. Image Suggestion:
Labeled macrophoto of common pests in greenhouses. Hydroponics in the greenhouse Hydroponics—growing plants without soil—pairs perfectly with greenhouse gardening.
Advantages:
faster rates of growth. More profits per square foot. Lower water usage. Common Aquaponic Systems: Nutrient Film Technique (NFT).
Culture in Deep Water (DWC) Systems of flow and ebb. Idea for an image: Photo of a hydroponic setup inside a greenhouse.
Methods of Sustainable Gardening in Sheds Modern greenhouse gardening can be very good for the environment: Make use of solar panels to generate clean energy. Install systems for capturing rainwater.
Utilize organic pest management methods. Idea for an image: A picture of a greenhouse powered by the sun that has a tank for collecting rainwater. Beginning Greenhouse Gardening If you’re just starting out, follow these simple tips:
Begin small with simple crops. Keep a greenhouse journal to track plant progress.